What is modem?
A modem is a hardware device that allows a computer to
send and receive data over a telephone line or a cable or satellite connection.
In the case of transmission over an analog telephone line, which was once the
most popular way to access the internet, the modem converts data between analog
and digital formats in real time for two-way network communication. In the case
of the high-speed digital modems popular today, the signal is much simpler and
doesn't require the analog-to-digital conversion.
Different Types of Modem :
Dial-Up Modem
Traditional modems used on dial-up networks convert data
between the analog form used on telephone lines and the digital form used on
computers. An external dial-up modem plugs into a computer at one end and a
telephone line on the other end. In the past, some computer makers integrated
internal dial-up modems into their computer designs.
Modern dial-up network modems transmit data at a maximum
rate of 56,000 bits per second. However, inherent limitations of public
telephone networks often limit modem data rates to 33.6 Kbps or lower in
practice.
When connecting to a network via a dial-up modem, the
devices customarily relay through a speaker the distinctive sounds created by
sending digital data over the voice line. Because the connection process and
data patterns are similar each time, hearing the sound pattern helps a user
verify whether the connection process is working.
 |
| Figure: Dial-Up Modem |
Broadband Modem
A broadband modem like those used for DSL or cable
internet access uses advanced signaling techniques to achieve dramatically
higher network speeds than traditional dial-up modems. Broadband modems are
often referred to as high-speed modems. Cellular modems are a type of digital
modem that establishes internet connectivity between a mobile device and a cell
phone network.
External broadband modems plug into a home broadband
router or other home gateway device on one end and the external internet
interface such as a cable line on the other. The router or gateway directs the
signal to all the devices in the business or home as needed. Some broadband
routers include an integrated modem as a single hardware unit.
Many broadband internet providers supply suitable modem
hardware to their customers at no charge or for a monthly fee. However,
standard modems can be purchased through retail outlets.
 |
| Figure: Broadband Modem |
Voice modem
Voice modems are regular modems that are capable of
recording or playing audio over the telephone line. They are used for telephony
applications. See voice modem command set for more details on voice modems.
This type of modem can be used as an FXO card for private branch exchange (PBX)
systems.
 |
| Figure: Voice Modem |
Optical modem
An optical modem is a key device that modulates Ethernet digital signals to optical fibers. It is connected to a computer using a network cable and connected to the remote office of a carrier using an optical fiber. Generally, an ONU that uses the PON technology is a common optical modem, and certainly there are other optical modems that do not use the PON technology.
Fiber optic systems can be upgraded by the use of
quadrature amplitude modulation. The modulator and demodulator are separate
components rather than a single assembly as with most modems.
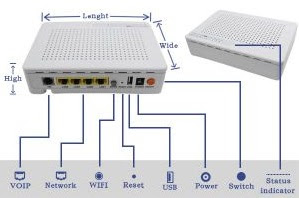 |
| Figure: Optical Modem |
----Thank You----


0 Comments